A spermatocele is a dense and voluminous formation that has fibrous membrane, a rounded shape and sometimes contains fluid with an admixture of spermatozoa.
A spermatocele can also be a sign of a dangerous pathology, such as a tumor of the testicle or the ducts through which sperm passes. Therefore, it is necessary for a doctor to check any formation in the scrotum and inguinal canal..
A scrotal cyst or funicocele does not in itself cause infertility. The cyst grows quite quickly and can cause infertility by putting pressure on surrounding tissues, including normally functioning ducts. Especially in bilateral development.
In most cases, testicular cysts grow slowly, do not cause complications and do not affect a man’s sexual activity or reproductive function at all.
Patients complain of an additional formation in the scrotum, which is easily palpable, not painful and does not manifest itself in any way. Rarely, if the cyst is large or growing rapidly, there may be an uncomfortable feeling of pressure in the scrotum. There may also be a discomfort when sitting and walking.
Congenital cysts are associated with a violation of the development of the embryo. Such spermatogenic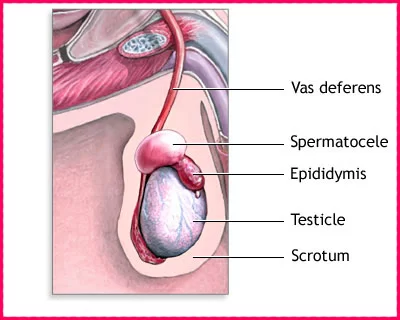 spermatocele – an illustration of a cyst filled with a clear liquid without sperm. Acquired cysts develop as a result of trauma or inflammatory diseases of the scrotum.
spermatocele – an illustration of a cyst filled with a clear liquid without sperm. Acquired cysts develop as a result of trauma or inflammatory diseases of the scrotum.
Damaged or inflamed ducts cease to function normally and become clogged, as a result of which sperm production stops. A secret accumulates, which, in turn, stretches the walls of the vas deferens. Under these conditions, cavities (cysts) are formed, which turn out to be new or decayed spermatozoa.
A spermatocele is a painless, round, firm, elastic mass in the head, tail, or vas deferens of the epididymis.
To clarify the diagnosis of spermatocele doctors are using instrumental methods:
- Diaphanoscopy;
- Ultrasonography;
- Computed tomography or nuclear magnetic resonance imaging.
Testicular cyst is safe for health. Treatment is required when it becomes painful or becomes so large that the scrotum is greatly enlarged and interferes with sitting or moving.
For small cysts, most urologists recommend waiting. If the cyst deforms surrounding tissues, then surgery becomes necessary.
As a rule, the prognosis is favorable. and impaired reproductive function restores.