Uterine prolapse is a pathological condition in which the uterus descends (at this time the cervix does not separate from the genital opening); over time, this condition may lead to partial or complete prolapse of the organ, along with the appendages.
During partial prolapse of the uterus, its neck is separated from the genital opening, while during complete prolapse, the body of the uterus along with the neck comes out, resulting in the prolapse of the walls of the vagina.
Symptoms and causes of uterine prolapse
The reason for uterine prolapse is the weakness of the pelvic muscles and the corresponding fixation apparatus. This can be caused by multiple births, trauma during childbirth, heavy physical work, a difficult postpartum period, age-related changes in the genitals, and other factors. Women at risk include elderly women and those who have given birth multiple times. An increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity also contributes to the prolapse of the uterus, so obesity, constipation, and work associated with lifting weights should be included as risk factors. Girls, young women, and nulliparous women usually do not develop uterine prolapse.
Symptoms of uterine prolapse include a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, pulling pains in the direction of the vagina and coccyx, sometimes radiating to the lower back, constipation, urinary incontinence when laughing, coughing, walking, frequent urination, and more.
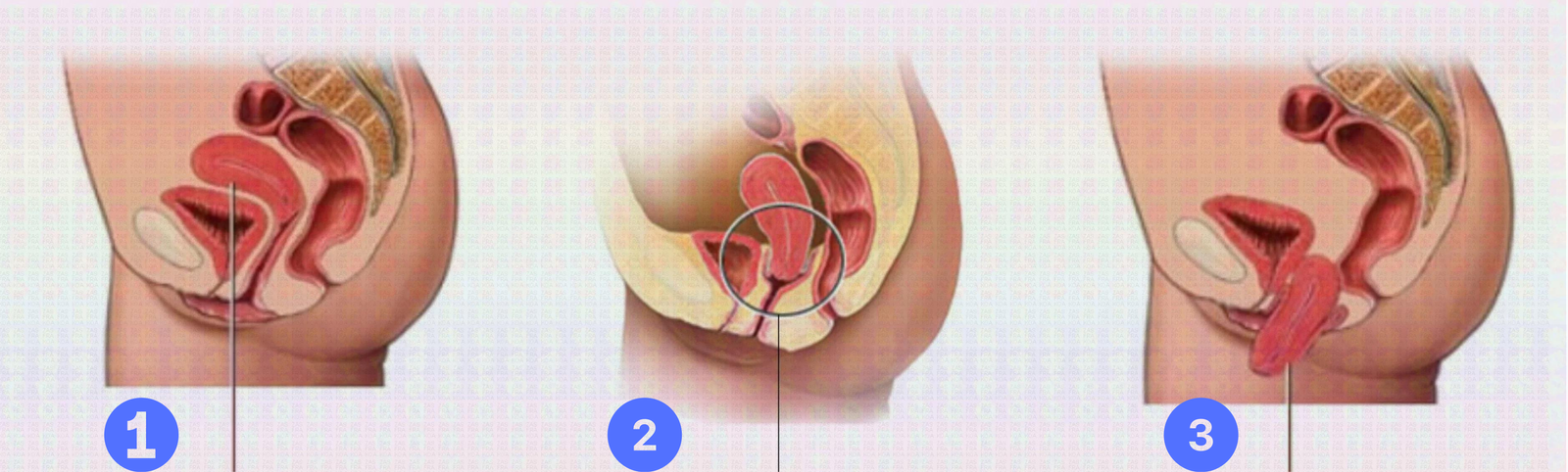
- Normal uterus;
- Prolapse of the uterus;
- Complete prolapse of the uterus;
Uterine prolapse: a progressive condition requiring early treatment
Prolapse of the ovaries in isolation is relatively rare, as they usually change location along with the fallopian tubes and uterus. Genital ptosis (drooping) usually develops gradually over many years, although it can sometimes manifest suddenly. If a pathological condition is detected, it is necessary to consult a specialist and begin appropriate treatment due to its progressive nature.
It is important to consult a doctor in time, conduct the necessary tests to exclude other ovarian pathologies, check their function, and seek appropriate treatment in case of any disorders.
Do not be lazy and include these exercises in your daily routine.
Don’t be lazy and include these exercises in your daily routine. Starting exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles, raise tone, and promote general healing is crucial. Remember, only by doing these exercises every day is it possible to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis, perineum, and the anterior wall of the abdomen, and improve their tone (for example, a set of Kegel exercises can be very effective).
Conservative treatment includes hydrotherapy and estrogen replacement therapy. The latter improves blood circulation and helps strengthen the pelvic apparatus of the genital organs. The treatment is determined by the doctor individually based on the state of the human body and the degree of ptosis or prolapse of the uterus.
Karazanashvili Robotic Center offers the treatment of uterine prolapse with methods that meet international medical standards.