Urethritis or inflammation of the urethra – sexually transmitted diseases often cause urinary disorders. At this time, patients complain of painful urination. Symptoms of urethritis often appear after infection with a sexually transmitted disease – itching and burning when urinating.
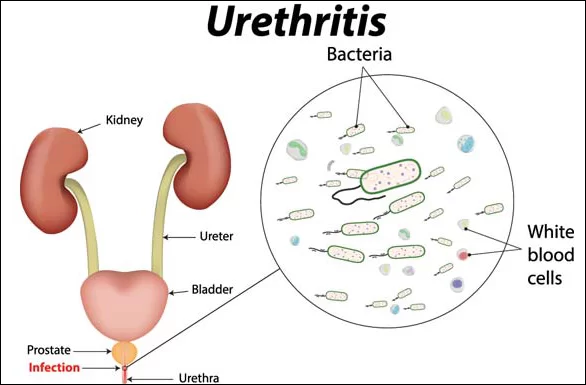
Urethritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra, which occurs in both women and men. Infectious urethritis is often caused by sexually transmitted infections. There are two forms: acute and chronic.
Acute urethritis develops a few days after infection. Chronic inflammation is the result of uncontrolled or improperly treated acute inflammation.
Signs of urethritis that developed with sexually transmitted diseases are:
- Discharge from the penis (urethra) is thick, cloudy, often of different colors (gray, greenish, etc.);
- Itching, burning and cutting pains when urinating.
Often, the symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases, discharge and urination disorders disappear after the acute stage has passed. The patient thinks disease is gone. In fact, the infection did not disappear anywhere, it simply “hid”, turned into a chronic form. Although sometimes it does not bother a person at all, a chronic venereal disease, it continuously causes irreparable harm to the body.
However, with improper treatment of acute urethritis, diseases such as prostatitis may develop in the future. Also epididymitis, erosion or swelling of the cervix, pyelonephritis and others. Therefore, at the first signs of urethritis, it is better to consult a doctor.
Genital discharge can be observed with gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, nonspecific urethritis.
We talk about physiological conditions in which the presence of specific secretions is not considered a pathology.
During an erection, a specific secretory fluid is often released from the opening at the top of the penis. It is not at all like the one that comes out during ejaculation. This liquid comes in the form of a transparent drop and performs the function of anointing the beginning of the letter. In addition, it reduces the acidity of the urethra so that the male ejaculate fertilizes the female. Men sometimes mix a drop of urine with this secretory fluid. It is very easy to distinguish them: urine is like water, and the secretory fluid is sticky, even viscous.
The second physiological state is pollution. Contamination is the accidental spillage of seminal fluid. Such things usually happen during sleep in the background of erotic dreams and do not interrupt our sleep. Pollution is common in teenagers and young adults and is indicative of puberty. As soon as regular sex life begins, pollution stops. There is also daytime pollution. Pollution is not a deviation from the norm, but an indicator of the normal hormonal activity of the gonads. If this happens often, this indicates a violation of the sexual sphere, and at this time a visit to the doctor is necessary. All other secretions that flow from the male genital organs should be examined by a specialist doctor.
Urethritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra). Discharge from the urethra is considered a characteristic symptom of urethritis in men. But the discharge can be physiological. be, and urethritis proceeds without discharge, therefore it is of great importance to consult a doctor as soon as discharge is noticed. Urethritis, in addition to discharge, is usually accompanied by dysuria and irritation of the penis. It is diagnosed by examination of the urethral smear or the first portion of urine and is often caused by gonococci, chlamydial infection, and others.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea occurs differently in women and men. Common to him is that the main manifestation of the disease is associated with discharge from the genital organs and sharp pains during urination.
This is a sign of urethritis, an inflammation of the urethra caused by an infection. White or yellow discharge from the penis is considered a symptom of gonorrhea in men, but if there is no discharge, this does not mean that the person is not sick. Allocations usually appear after the incubation period. It should also be borne in mind that sometimes the incubation period is delayed.
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of cases of asymptomatic gonorrhea. In other cases, after the incubation period, symptoms characteristic of the acute form of gonorrhea appear.
The course of the disease and the manifestation of symptoms depend primarily on which organ the gonococcus attacks. Most often, the disease damages the urethra and gonorrheal urethritis develops. By the way, it is also characterized by discharge, leaving yellowish-green spots on the linen.
Gonorrhea. This is a rather serious infection that causes infertility, impotence, and other complications if left untreated. Modern medicine is very easy to cope with its cause. The main thing is to start treatment as early as possible, and self-medication can complicate the situation.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas is a unicellular organism that can live not only inside the body but also outside it. In addition to the harm Trichomonas can cause, it also has the ability to ingest gonococci without causing harm.
When transmitted from one person to another, Trichomonas also carry “swallowed” gonococci. With incomplete treatment, gonorrhea infection develops after treatment for trichomoniasis.
Trichomoniasis in men is often asymptomatic. A man can be a carrier of infection all his life, infecting his partners, but he himself does not experience any discomfort. Relatively rarely, the inflammatory process manifests itself in the urethra, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles, testicles. Sometimes there is cloudy white fluid from the urethra or traces of blood in the urine. It lasts 1-2 weeks. Then the symptoms decrease, but the disease continues and becomes chronic.
Ureaplasmosis
Ureaplasma is a microorganism that is considered a transitional step from viruses to unicellular organisms.
Infection with this organism is often sexually transmitted. Additionally, the mother can transmit it to her child during childbirth.. The incubation period of the disease is from 4 days to a month, rarely longer. After the incubation period, the first symptoms of ureaplasmosis appear.
It should be said that often ureaplasmosis proceeds almost imperceptibly, and sometimes no symptoms are observed. These things are more common in women.
The most common symptoms of ureaplasmosis in men are scanty clear discharge from the penis, moderate pain and burning sensation when urinating. If the ureaplasma damaged the real gland, signs of prostatitis will come to light.
Mycoplasmosis
Urogenital mycoplasmosis clinically differs little from lesions of other etiologies. Some do not have subjective symptoms, others complain of a whole range of symptoms. When the urinary tract is affected in men, they observe slight discharge in the morning.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is gradually usurping the title of plague of the twenty-first century from other sexually transmitted diseases. According to WHO, the spread of this infection is comparable to the speed of an avalanche. This disease is mainly transmitted sexually. Every second urethritis in men is caused by chlamydia. A symptom of chlamydia in men is discharge from the urethra.
A small amount of discharge is accompanied by a slight pain during urination. In children (boys), along with discharge from the urethra, itching of the genital organs is also observed.
Nonspecific urethritis
Nonspecific urethritis is an inflammation of the urinary tract. Gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas, and other microorganisms, except for the herpes virus, cause inflammation. This is the most interesting and little-studied area of venereology. Suspicion of non-specific urethritis is necessary for any symptoms of urethritis.
Gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis is a dysbacteriosis of the vagina, so some experts believe that we cannot directly spread this pathology to men. However, it is also a fact that gardnerella, the causative agents of gardnerellosis, have the ability to cause inflammatory processes in the male body.
Gardnerella enters the male reproductive system directly during sexual contact. Because it is not a “legal resident” of its genital tract, we can consider it as a sexually transmitted disease.
Gardnerella is most often found in the male body and leaves the reproductive system usually after 2-3 days. Rarely, a chronic carrier of Gardner’s disease develops, in which the tests are always positive, although there are no symptoms of the disease. In 9 out of ten cases, gardnerella does not manifest itself in any way. And this is dangerous, because a man’s sexual partners get sick without even knowing it.
In classical cases, pathogens cause a sluggish inflammatory process of the mucous membrane. At this time, green discharge may come out of the penis, less disturbing to the patient. However, gardnerellosis can worsen the condition by causing urethritis, which manifests as burning and pain during urination.
In addition, the discharge from the letter has a specific smell. In such cases, it is necessary to treat gardnerellosis, and in other cases, many experts do not consider it necessary to treat gardnerellosis in men.
Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases in women
In women, these symptoms are mild. Most of the time, the disease is practically asymptomatic or the patient experiences symptoms that are typical for the entire group of sexually transmitted diseases.
Diagnosing sexually transmitted diseases cannot rely solely on symptoms as many of these diseases share similar symptoms.
There are warning signs that point to a particular disease. This:
- Unusual vaginal discharge. (white, slimy, hot, frothy, with or without odor);
- Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- Itching or burning in the genital area;
- Spotting from the vagina in the middle of menstruation;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- More frequent urination or a need to urinate than usual;
- Increase in body temperature. (maybe not even uniform or slightly increased within 370 s);
- Pain and itching when urinating;
- Pain during intercourse;
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Groin pain.
It is better to consult a gynecologist with a seemingly minor violation of urination or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Prevention of all the above diseases is very simple and effective:
A healthy lifestyle, fidelity to a partner, healthy eating, avoidance of fatigue and stress, a little attention to yourself will save you from many troubles. If the highlights from the email have changed, don’t expect it to go away on its own.
Only a specialist, urologist and andrologist, venereologist and gynecologist can accurately assess whether this is normal or not. Be sure to consult your doctor and make sure you are healthy